

The Wildland Fire Chemical Systems (WFCS) Program tests a variety of fixed- and rotary-wing airtankers to determine the parameters for optimal ground-pattern coverage over a wide range of fuel and fire conditions. The National Guard Sikorsky S-70 (military version is the UH-60) Black Hawk helicopter with the 660-gallon SEI Industries Bambi helibucket (referred to as the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket) is one of a family of helicopters designed for fire suppression with a helibucket. It is qualified as a Type 1 helicopter (figure 1).
 |
| Figure 1-The National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket. |
The helibucket is constructed of a heavy, coated fabric mounted to a collapsible frame. The dump valve (20 inches in diameter) is electrically actuated from the helicopter using 28 volts dc aircraft power. The bucket's maximum volume is 660 gallons with a maximum fill height of 53 inches. The volume of a given drop can be controlled by the rate at which the helibucket is lifted from the water (faster lift produces more volume) or by adjusting a cinch strap inside the helibucket.
The Missoula Technology and Development Center tested the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket with a series of drops over an array of plastic bowls much like Cool Whip containers. The quantity of material in each bowl was measured and the data were used to determine the drop pattern.
Tests included airspeeds from 40 to 88 knots (46 to 101 miles per hour) and drop heights from 73 to 170 feet from the bottom of the tank to the ground. The drops were made with three different materials: water, foam, and gum-thickened retardant.
Flow rate, drop height, and airspeed all affect the drop pattern. Because this type of helicopter is normally used over a narrow range of heights and speeds and because this system produces a single flow rate, information about an average drop is presented. Figures 2, 3, and 4 show the effect of drop height while maintaining airspeeds between 57 to 59 knots (65 to 68 miles per hour) with drop heights ranging from 83 to 128 feet while using gum-thickened retardant. Figures 5, 6, and 7 show the effect of increasing airspeed from 42 to 81 knots (48 to 93 miles per hour) while maintaining the drop height between 138 and 149 feet.
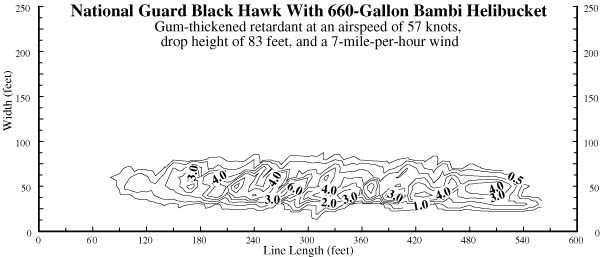 |
| Figure 2-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using gum-thickened retardant at an airspeed of 57 knots (66 miles per hour) and a drop height of 83 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
 |
| Figure 3-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using gum-thickened retardant at an airspeed of 56 knots (64 miles per hour) and a drop height of 117 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
 |
| Figure 4-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using gum-thickened retardant at an airspeed of 59 knots (68 miles per hour) and a drop height of 128 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
 |
| Figure 5-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using water at an airspeed of 42 knots (48 miles per hour) and a drop height of 138 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
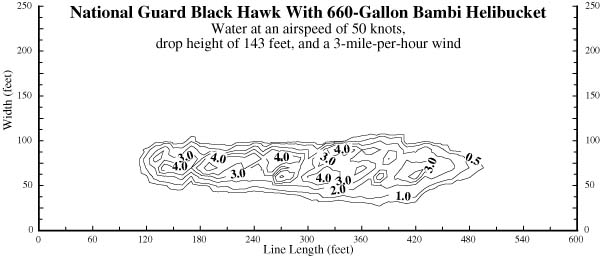 |
| Figure 6-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using water at an airspeed of 50 knots (58 miles per hour) and a drop height of 143 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
 |
| Figure 7-Drop pattern characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucketusing water at an airspeed of 81 knots (93 miles per hour) and a drop height of 149 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
The proper amount of fire-retarding materials to be applied (expressed as coverage level in gallons per 100 square feet) differs depending on the fuel model. Table 1 shows the coverage needed for specific fuel models using both the National Fire Danger Rating System (NFDRS) and Fire Behavior Fuel Model descriptions.
Table 1-The retardant coverage needed for specific fuel types.
| Fuel Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| National Fire Danger Rating System (NFDRS) | Fire Behavior | Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) | Description |
| A, L, S | 1 | 1 | Annual and perennial western grasses, tundra |
| C | 2 | Conifer with grass | |
| H, R | 8 | 2 | Shortneedle closed conifer; summer hardwood |
| E, P, U | 9 | Longneedle conifer; fall hardwood |
|
| T | 2 | Sagebrush with grass | |
| N | 3 | Sawgrass | |
| F | 5 | 3 | Intermediate brush (green) |
| K | 11 | Light slash | |
| G | 10 | 4 | Shortneedle conifer (heavy dead litter) |
| O | 4 | Southern rough | |
| F, Q | 6 | 6 | Intermediate brush (cured), Alaska black spruce |
| B, O | 4 | California mixed chaparral, high pocosin |
|
| J | 12 | Greater than 6 | Medium slash |
| I | 13 | Heavy slash | |
The results of drop tests allow managers to estimate the length of line a specific helicopter with a particular bucket produces at various coverage levels. Table 2 or figures 8 and 9 can be used to determine the drop height and airspeed of a water drop required to obtain the longest line at each coverage level. Table 3 or figures 10 and 11 can be used to determine the drop height and airspeed of a foam drop required to obtain the longest line at each coverage level. Table 4 or figures 12 and 13 can be used to determine the drop height and airspeed of a gum-thickened retardant drop required to obtain the longest line at each coverage level.
Table 2-Water tests producing the longest line at various coverage levels.
| Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) | Line Length (feet) |
Drop Height (feet) |
Airspeed (knots) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 528 | 111 | 84 |
| 1 | 502 | 111 | 84 |
| 2 | 385 | 111 | 84 |
| 3 | 350 | 92 | 60 |
| 4 | 285 | 102 | 46 |
| 6 | 216 | 78 | 40 |
| 8 | 202 | 78 | 40 |
| 10 | 176 | 78 | 40 |
 |
| Figure 8-Use this graph to estimate the drop height needed to provide the longest line of water at various coverage levels. |
 |
| Figure 9-Use this graph to estimate the airspeed needed to provide the longest line of water at various coverage levels. |
Table 3-Foam tests producing the longest line at various coverage levels.
| Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) | Line Length (feet) |
Drop Height (feet) |
Airspeed (knots) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 533 | 118 | 80 |
| 1 | 447 | 107 | 82 |
| 2 | 333 | 92 | 61 |
| 3 | 295 | 92 | 61 |
| 4 | 231 | 92 | 61 |
| 6 | 176 | 92 | 41 |
| 8 | 105 | 92 | 41 |
| 10 | 32 | 92 | 41 |
 |
| Figure 10-Use this graph to estimate the drop height needed to provide the longest line of foam at various coverage levels. |
 |
| Figure 11-Use this graph to estimate the airspeed needed to provide the longest line of water at various coverage levels. |
Table 4-Gum-thickened retardant tests producing the longest line at various coverage levels.
| Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) | Line Length (feet) |
Drop Height (feet) |
Airspeed (knots) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 487 | 131 | 79 |
| 1 | 462 | 83 | 57 |
| 2 | 399 | 83 | 57 |
| 3 | 363 | 83 | 57 |
| 4 | 313 | 83 | 57 |
| 6 | 231 | 86 | 48 |
| 8 | 189 | 86 | 48 |
| 10 | 123 | 86 | 48 |
 |
| Figure 12-Use this graph to estimate the drop height needed to provide the longest line of gum-thickened retardant at various coverage levels. |
 |
| Figure 13-Use this graph to estimate the airspeed needed to provide the longest line of gum-thickened retardant at various coverage levels. |
The line-length graphs predict line length (in feet) as a function of drop height (in feet) and airspeed (in knots). The tables are constructed by selecting the drop producing the longest line at each coverage level. Either the graphs or tables may be used to estimate the drop height and airspeed required to produce the longest line for a given coverage level. The tables show an ideal case, while the graphs represent an average.
 |
| Figure 14-Drop test of the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket using water. |
For example, if a fire is burning in NFDRS Fuel Model H, R (Fire Behavior Model 8), represented by shortneedle closed conifer or summer hardwood, table 1 shows that a coverage level of 2 is required. The table for gum-thickened retardant (table 4) shows that for coverage level 2, a drop height of approximately 83 feet and airspeed of 57 knots (66 miles per hour) produces the longest line (399 feet).
The ground drop characteristics for the National Guard Black Hawk with 660-gallon Bambi helibucket were derived through controlled test drop procedures on flat ground (figure 14). This information is to serve only as a guide in assisting field personnel to determine the proper drop height and airspeed for delivering water, foam, or gum-thickened retardant. Actual coverage may vary depending on terrain, wind, weather, and pilot proficiency.
Cammie Jordan is a Project Assistant for the Wildland Fire Chemical Systems Program at MTDC. She is an elementary education student at the University of Montana and has worked for MTDC since 1998.
Paul Solarz is Program Leader for the Wildland Fire Chemical Systems Group. He received his bachelor's degree from Eastern Oregon State College in 1986. Paul has worked in Aviation and Fire Management since 1973, serving at seven Ranger Districts and in two Forest Supervisor's offices. He has an extensive operational background in fire, fuels, and aviation.
Additional single copies of this document may be ordered from:
USDA Forest Service
Missoula Technology and Development Center
5785 Highway 10 West
Missoula, MT 59808
Phone: 406-329-3978
Fax: 406-329-4811
E-mail: wo_mtdc_pubs@fs.fed.us
For additional Information contact:
Greg Lovellette, Project Leader
Missoula Technology & Development Center
5785 Highway 10 West
Missoula, MT 59808
Phone: 406-329-4719
Fax: 406-329-4811
E-mail: glovellette@fs.fed.us
Lotus Notes: Greg Lovellette/WO/USDAFS
This page last modified June 14, 2002
Visitor
since June 14, 2002