

The Wildland Fire Chemical Systems (WFCS) program tests a variety of fixed- and rotary-wing tankers to determine the parameters for optimal coverage over a wide range of fuel and fire conditions. The Aero Flite DC-4 (also known as the C-54E) with a modified conventional tank manufactured by ARDCO is one of a family of multiengine airtankers designed for fire suppression as a Type 2 airtanker.
The Missoula Technology and Development Center tested the Aero Flite DC-4 (Figure 1) with a series of drops over an array of plastic bowls much like Cool Whip containers. The quantity of material in each bowl was measured and the data were used to determine the drop pattern.
 |
| Figure 1-A static test of the Aero Flite DC-4 airtanker. |
The modified conventional tank is constructed of aluminum. The door opening is actuated by an independent hydraulic system mechanically activated using 28-volt dc aircraft power with a Black Hills-type controller. The tank is certified to hold 2000 gallons. It has eight compartments and eight doors arranged with four compartments forward and four to the rear. Each compartment contains deployable flow restrictors to help control flow rate. Restrictors serve as a physical barrier that lowers the flow rate as liquid is released from the tank (Figure 2). Tests included airspeeds from 121 to 139 knots (139 to 160 mph) and drop heights from 172 to 488 feet (measured from the bottom of the tank to ground). The drops were made with two different materials: water and gum-thickened retardant.
 |
| Figure 2-Drop pattern characteristics for the Aero Flite DC-4 with a restricted modified conventional tank using 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant with an airspeed of 135 knots (155 mph) at a drop height of 217 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
Flow rate, drop height, and airspeed all have an effect on the drop pattern. Increasing drop height gradually widens the drop at the expense of higher coverage levels. This effect is modified by the ambient wind. Increasing wind speed widens the drop and decreases coverage levels.
Airspeed has a much greater effect on the drop pattern. Because restrictors allow flow to be varied in each compartment in the ARDCO tank the Aero Flite DC-4 can be configured for specific coverage levels by raising or lowering restrictors and releasing more than one compartment at a time. Figures 3 and 4 show the effect of using restricted or unrestricted flow setting while dropping 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant. These drops included airspeeds of 134 and 135 knots (154 and 155 mph) and drop heights of 201 to 217 feet (measured from the bottom of the tank to the ground).
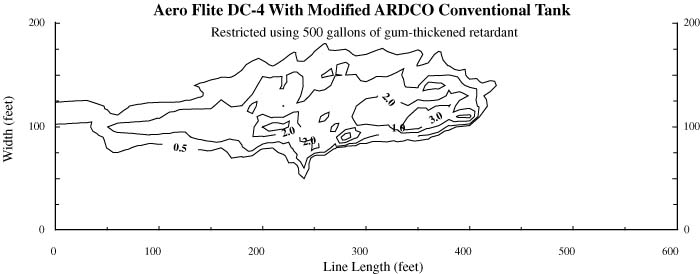 |
| Figure 3-Drop pattern characteristics for the Aero Flite DC-4 with an unrestricted modified conventional tank using 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant with an airspeed of 134 knots (154 mph) and a drop height of 201 feet. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 per 100 square feet. |
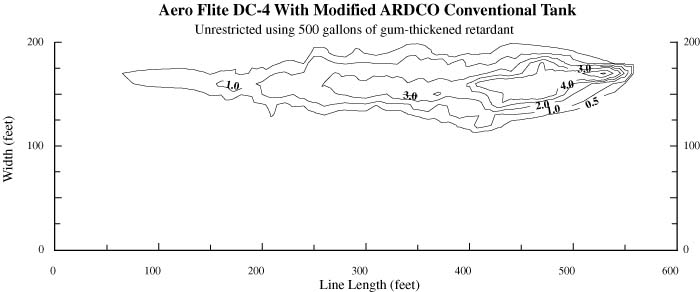 |
| Figure 4-Drop pattern characteristics for the Columbia BV-234 using the modified 3000-gallon Griffith helibucket dropping gum-thickened retardant at an airspeed of 53 knots (61 mph), drop height of 73 feet, and flow rate of 200 gallons per second. The contour lines are at coverage levels of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 10 gallons per 100 square feet. |
The proper amount of fire-retarding material to be applied (expressed as coverage level in gallons per 100 square feet) differs depending on the fuel model. Table 1 shows the coverage needed for specific fuel models using both the National Fire Danger Rating System (NFDRS) and the Fire Behavior Fuel Model descriptions.
Table 1-The retardant coverage needed for specific fuel types.
| Fuel Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| National Fire Danger Rating System (NFDRS) | Fire Behavior | Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) | Description |
| A, L, S | 1 | 1 | Annual and perennial western grasses, tundra |
| C | 2 | Conifer with grass | |
| H, R | 8 | 2 | Shortneedle closed conifer; summer hardwood |
| E, P, U | 9 | Longneedle conifer; fall hardwood |
|
| T | 2 | Sagebrush with grass | |
| N | 3 | Sawgrass | |
| F | 5 | 3 | Intermediate brush (green) |
| K | 11 | Light slash | |
| G | 10 | 4 | Shortneedle conifer (heavy dead litter) |
| O | 4 | Southern rough | |
| F, Q | 6 | 6 | Intermediate brush (cured), Alaska black spruce |
| B, O | 4 | California mixed chaparral, high pocosin |
|
| J | 12 | Greater than 6 | Medium slash |
| I | 13 | Heavy slash | |
The results of drop tests allow managers to estimate the length of line a specific airtanker produces at various coverage levels. With conventional airtankers, trail drops are performed to produce different line lengths of the desired coverage levels. The time intervals between simultaneous releases of two compartments that produced the maximum length of line of the desired coverage level were determined by using computer simulation and drop test data. Drop height, airspeed, and wind speed also affect the drop pattern. Table 2 or Figure 5 demonstrates restricted gum-thickened retardant test drops producing the maximum line length of the desired coverage level based on varying the time interval during a 2 x 4 trail drop. A 2 x 4 trail drop refers to two compartments opening simultaneously, followed by a preset delay, before two more compartments open simultaneously, until eight compartments have been released (two doors at a time, for four times). Table 3 or Figure 6 demonstrates unrestricted gum-thickened retardant test drops producing the maximum line length of the desired coverage level based on varying the of time interval during a 2 x 4 trail drop.
Table 2-Maximum line length based on varying the of time interval of a computer-simulated restricted 2 x 4 trail drop, with an airspeed of 135 knots and a wind speed of 9 mph at a height of 217 feet. This restricted drop used 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant.
| Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) |
Time Interval Between Releases (seconds) |
Line Length (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 2.12 | 1720 |
| 1 | 1.73 | 1410 |
| 2 | 0.69 | 690 |
| 3 | 0.39 | 490 |
| 4 | 0.49 | 410 |
| 6 | 0.25 | 280 |
| 8 | 0.15 | 190 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 90 |
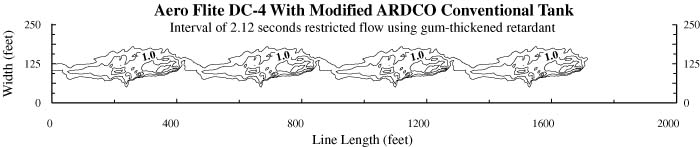 |
| Figure 5-Drop pattern characteristics for the Aero Flite DC-4 with a restricted conventional tank using 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant with a computer-simulated restricted 2 X 4 trail drop (dropping compartments 1 and 2 four times) with a time interval of 2.12 seconds. |
Table 3-Maximum line length based on varying the time interval of a computer-simulated unrestricted 2 x 4 trail drop, with an airspeed of 134 knots and a wind speed of 6 mph at a height of 201 feet. This unrestricted drop used 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant.
| Coverage Level (gal/100 sq. ft) |
Time Interval Between Releases (seconds) |
Line Length (feet) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 2.45 | 2000 |
| 1 | 1.83 | 1470 |
| 2 | 1.43 | 1170 |
| 3 | 0.74 | 730 |
| 4 | 0.69 | 650 |
| 6 | 0.69 | 430 |
| 8 | 0.20 | 310 |
| 10 | 0.15 | 260 |
 |
| Figure 6-Drop pattern characteristics for the Aero Flite DC-4 with an unrestricted modified conventional tank using 500 gallons of gum-thickened retardant with a computer-simulated unrestricted 2 X 4 trail drop (dropping compartments 1 and 2 four times) with a time interval of 2.45 seconds. |
To select the proper airtanker time interval, for trail drops, first use Table 1 to determine the coverage level required by the National Fire Danger Rating System or Fire Behavior Fuel Models. The coverage levels in Table 1 represent the coverage level required for average fire intensity for each fuel model. The required coverage level can be adjusted up or down depending on the actual fire intensity. Once the required coverage level is determined, a time interval can be found.
For example, if a fire is burning in NFDRS Fuel Model G (Fire Behavior Model 10), represented by short-needle conifer (heavy dead litter), Table 1 shows that a coverage level of 4 is required. The table for gum-thickened retardant shows that for coverage level 4 an unrestricted 2 x 4 trail drop (Table 3) produces the longest line length of 650 feet when the time interval between releases is 0.69 seconds.
 |
| Figure 7-Gum-thickened retardant dropped by the Aero Flite DC-4 airtanker. |
The ground drop characteristics for the Aero Flite DC-4 were derived through controlled drop test procedures (Figure 7) on flat ground. The time intervals were derived through computer simulation by overlaying the drop pattern produced from simultaneous releases of compartments 1 and 2. This information is to serve only as a guide in assisting field personnel to determine the proper drop height, airspeed, and door opening for delivering water or gum-thickened retardant. Actual coverage may vary depending on terrain, wind, weather, and pilot proficiency.
Cammie Jordan is a Project Assistant for the Wildland Fire Chemical Systems Program at MTDC. She is an elementary education student at the University of Montana and has worked for MTDC since 1998.
Paul Solarz is Program Leader for the Wildland Fire Chemical Systems Group. He received his bachelor's degree from Eastern Oregon State College in 1986. Paul has worked in Aviation and Fire Management since 1973, serving at seven Ranger Districts and in two Forest Supervisor's offices. He has an extensive operational background in fire, fuels, and aviation.
Additional single copies of this document may be ordered from:
USDA Forest Service
Missoula Technology and Development Center
5785 Highway 10 West
Missoula, MT 59808
Phone: 406-329-3978
Fax: 406-329-4811
E-mail: wo_mtdc_pubs@fs.fed.us
For additional Information contact:
Greg Lovellette, Project Leader
Missoula Technology & Development Center
5785 Highway 10 West
Missoula, MT 59808
Phone: 406-329-4719
Fax: 406-329-4811
E-mail: glovellette@fs.fed.us
Lotus Notes: Greg Lovellette/WO/USDAFS
This page last modified June 12, 2002
Visitor
since June 12, 2002