Cougar
 Scientific Name: Puma concolor
Scientific Name: Puma concolor- Niimíipuu Name: ḱoỳaḿá
Traits and Behaviors:
Cougars are a solitary species that live around rocky cliffs, ledges, vegetated ridgetops, and areas where their prey is located. They are generally active at night and hunt deer, elk, moose, mountain goats, wild sheep, and deer. Younger cougars eat raccoons, coyotes, rabbits, hares, small rodents, and sometimes pets or livestock. Cougars will drag the prey to a covered area to feed on it and once full will hide the rest of the remains under snow, grass, leaves, or anything else available.

Cougars have den sites in dense thickets or under fallen logs. They use these dens during the day for sleep, general protection from the weather, and to raise their young. Their home range includes the area they hunt within, which varies by sex, age, and season. Home ranges can span up to 196 miles but can also be as small as 25 miles. Males have a larger range and can grow up to 8 feet long and 130-150 pounds. Females are around 7 feet long and weigh 65-90 pounds. If a cougar is in the area you will also notice scratches on logs or trees, scraped up piles of leaves or dirt, or large scats with hair and bones in it.
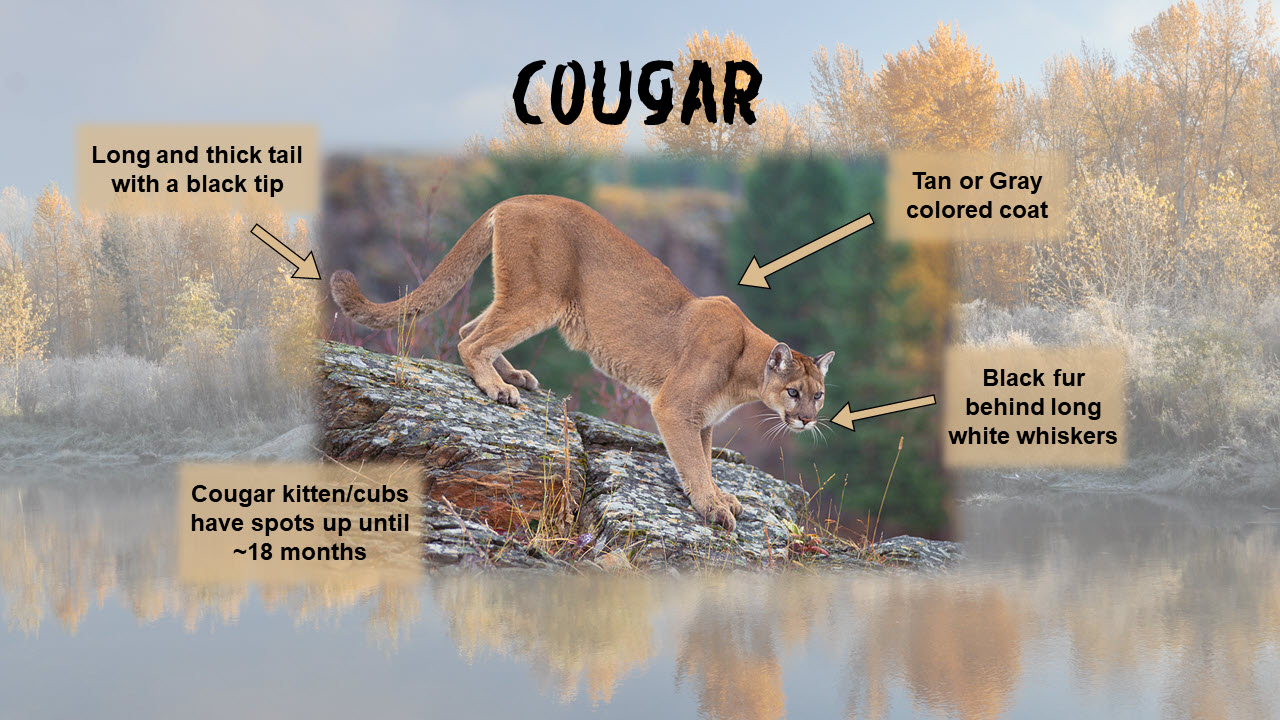
Cougars are a uniform color of tan or gray with a long thick tail with a black tip and black around the whiskers area. Kittens, or cubs, are covered in black or brown spots until the age of 18 months with about 1-6 kittens in each litter. Cougars are polygamous and breed year-round, so litters can be seen any time of the year, but most often in July and August.
Safety Tips:
To safely travel through the habitats that cougars live in, use these steps to avoid running into a cougar-
 Make a lot of noise! Cougars do not like to be surprised and will move away from human voices. You can also whistle or use bells.
Make a lot of noise! Cougars do not like to be surprised and will move away from human voices. You can also whistle or use bells.- Stay away from dead animals since this may be food the cougar has saved for later.
- Travel in small groups and do not leave food lying around.
- Avoid running or walking alone at dawn, dusk, or after dark.
- Stay aware of your surroundings (do not wear headphones and look for signs of a cougar).
If you still run into a cougar, follow these steps-
- Do not approach the cougar.
- Do not run or bend over.
- Make yourself appear large and intimidating.
- Face the cougar and back away slowly. Do not turn your back to them.
 Nez Perce Wéeyekin:
Nez Perce Wéeyekin:
The Nez Perce gathered strength for changing conditions using spirituality. One important component of this is the guardian spirit called a wéeyekin. This is a spirit that young adults try to obtain during a solitary venture into the woods. This spirit guides or warns individuals during extreme or dangerous situations. One could say as a general idea that k’oy’am’á “cougar” is considered part of the pantheon of animals eligible as wéeyekin “spirit guardian(s).” Cougar hides (with fur) often served as an accoutrement for personal or horse regalia. Or even as a bow quiver. Such uses regarded or symbolized the k’oy’am’á as a helper in life. Meat-eater wéeyekin “spirit guardian(s)”, like the cougar, were considered fierce.
The cougar, also called a mountain lion, puma, or panther, is the largest member of the cat family located in the Western United States and Canada. During pre-settlement times, the cougar could be found from coast to coast and from Canada down to southern Chile and Argentina. The cougar is the mascot for Washington State University in Pullman, WA where cougar sightings are often reported.

