Everyday Hazmat User's Training Guide
Section III Hazardous Materials Management (continued)
Combustible Liquids (continued)
Outdoor Storage
USDA Forest Service policy and regulations determine how to store combustible liquids outside of buildings on USDA Forest Service land. The primary considerations are the amount of combustible liquids being stored and how close they are to structures, property lines, and roads. Keeping the amount of combustibles stored below the permitted levels per group will avoid more complicated storage requirements. Empty containers previously used for combustible liquids must be stored as if they still contained a combustible liquid.
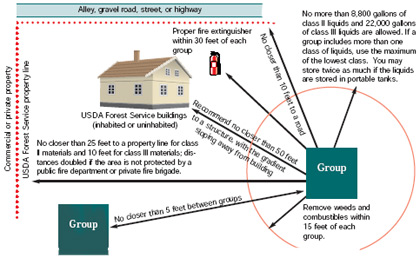
Click on image for larger descriptive view
Other Important Requirements
- Spill control and secondary containment are
required if any individual container has more than 55-gallon capacity or
the total capacity of all containers exceeds 1,000
gallons.
- All drums and portable tanks must be properly labeled.
- Each storage
area must have a NO SMOKING sign.
- All containers must be sound and tightly closed
at all times.
- Drums must be protected from the weather.
- Each group must be
protected from tampering; use guard posts to prevent vehicles from damaging
the stored materials.
- If a canopy or roof is used, the wall and supports must not
restrict more than 25 percent of the perimeter of the storage area, or
the configuration must be considered an inside storage area. Canopy and supports
must be of noncombustible
construction.
- Access must be available for firefighting equipment to reach each group.
Dispensing
Dispensing combustible liquids can be dangerous, especially in enclosed areas. Follow the regulatory restrictions on dispensing all combustible products and be sure to check with your local fire marshal to see if your area has more restrictive requirements.

Click on image for larger descriptive view
Other Important Requirements
- Do not dispense combustible liquids inside
a building unless the building
is specifically designed for indoor dispensing.
- Bond the container to the drum
before dispensing combustible liquids.
- Do not dispense combustible liquids
into a container in a plastic-lined
truck bed.
- Never pressurize the drum to aid in dispensing combustible liquids.
- Have
spill containment and cleanup materials readily available.
- Have the MSDS on
hand.
- Use secondary containment for drums when dispensing combustible liquids.
- Do
not dispense combustible liquids within 25 feet of an ignition source.
- Post
NO SMOKING signs in areas where you are dispensing combustible
liquids.
- Do not dispense combustible liquids near open flames or hot work.
- Do
not dispense combustible liquids within 25 feet of building openings, property
lines, alleys, or public ways.
- Use personal protective equipment as specified
by the MSDS.
- Combustible liquids can be gravity dispensed, but only if you
use a self-closing
or automatic-closing valve.
- Spill control and secondary containment are required
if:
- Combustible liquid is dispensed into a container exceeding 1.1 gallons.
- Any container exceeds 55 gallons or the total capacity of all containers inside a building exceeds 100 gallons.
- The capacity of all containers outdoors exceeds 5.3 gallons.
Transportation
The regulations for transporting combustible liquids are far less stringent than those for transporting flammable liquids. The primary concern is marking packages if you transport large quantities. Use the following guideline to identify some of these situations. If you plan to move combustible liquids by air, refer to the USDA Forest Service Interagency Aviation Transport of Hazardous Materials.
Pickup Trucks
- There are no special quantity, packaging, or operator restrictions
for transporting diesel on the highway in containers smaller than 119 gallons.
To transport diesel or other combustible liquids by air, see chapter 4
of the Interagency Aviation Transport of
Hazardous Materials.
- Diesel containers must be leak free, tightly closed, and
secured to the vehicle to prevent them from
moving during transportation.
- The transportation of combustibles other than
diesel
may not be exempt from DOT regulations.
- Drip-torch fuel is considered a flammable liquid because it contains gasoline. Flammable liquid regulations apply.
Vehicle Placard and ID Number
Placards and ID numbers are generally not required when transporting combustible liquids in containers smaller than 119 gallons, although it would be a good practice to use them.
 Flammable Liquid Placards (May be used when transporting combustible liquids.) |
 Vehicle Placard |

Identification Number
(Be sure to select the
proper number based on
the specific product.)
