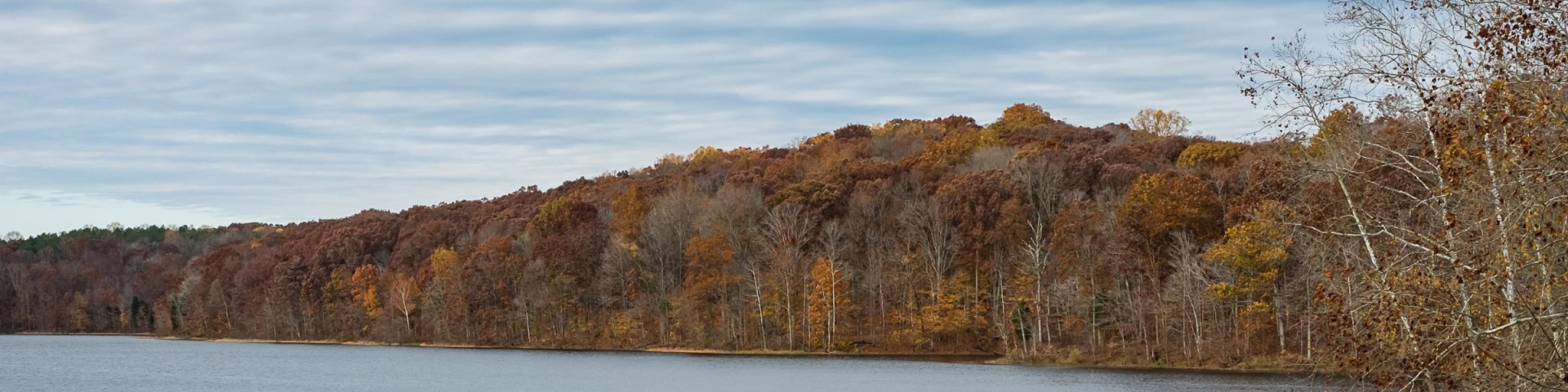
Welcome to Hoosier National Forest
Hoosier National Forest, in the hills of south central Indiana, provides a wide mix of opportunities and resources for people to enjoy. Rolling hills, back-country trails, and rural crossroad communities make this small but beautiful 204,000 acre Forest a local treasure.
Forest managers work with the public to develop a shared vision of stewardship focused on restoring, maintaining, and interpreting the cultural and natural resources of our public lands.
Quick Links
Alerts and Notices Rules and Regulations Get a Map Volunteer with Us
Community Resources
Current Projects Prescribed Fire Information Access to Terrill Cemetary Plant-A-Tree Program
Recreation Opportunities
Buffalo Springs Restoration Project – Public Engagement

As stewards of the land, we are entrusted by the American people to take a holistic look at forest ecosystems and make informed decisions about the future direction of those ecosystems and any needed management actions to improve conditions. An important part of that process is involving the local community, interested organizations, and forest visitors. This page is to share information about the Buffalo Springs Restoration Project and keep you updated on its status.
Photograph Your Forest Contest

The Hoosier National Forest is excited to announce a photo contest open to the general public! Come visit the Hoosier and capture spectacular views, special moments and hidden gems.