yellow buckeye (Aesculus flava)
Model Reliability: Low
| GCM SCENARIO | % Area Occ | Ave IV | Sum IV | Future/Current IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | 1.6 | 3.6 | 1682 | N/A |
| RFimp | 1.8 | 1.7 | 938 | 0.56 |
| CCSM45 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 815 | 0.87 |
| CCSM85 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 726 | 0.77 |
| GFDL45 | 2 | 1.2 | 707 | 0.75 |
| GFDL85 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 584 | 0.62 |
| HAD45 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 563 | 0.6 |
| HAD85 | 1.7 | 1 | 505 | 0.54 |
| GCM45 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 695 | 0.74 |
| GCM85 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 605 | 0.65 |
Regional Summary Tree Tables
Summaries for tree species are available for a variety of geographies, in both PDF and Excel format. These summaries are based on Version 4 of the Climate Change Tree Atlas
Interpretation Guide
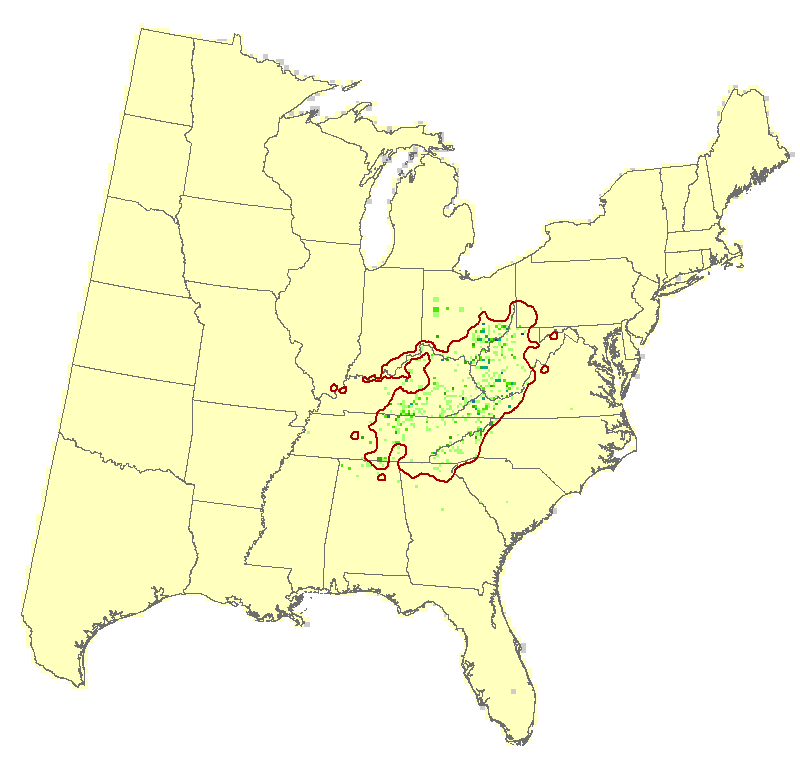
Yellow buckeye, like Ohio buckeye, is narrowly distributed (1.2% of area), sparse, and low IV, centered on the central states (e.g., West Virginia, Kentucky) and with a low reliability model projecting decline in suitable habitat. It also has low adaptability, being susceptible to drought, fire, and regeneration failure, thus also yielding a very poor capacity to cope. SHIFT shows some minor migration.
Family: Hippocastanaceae
Guild: opportunistic, dispersal limited
Functional Lifeform: large deciduous tree
| 3.1 | -0.03 |
| -2.13 |  |
MODFACs
What traits will impact yellow buckeye's ability to adapt to climate change, and in what way?:
Primary Positive Traits
Shade tolerance
Primary Negative Traits
Drought Seedling establishment Fire topkill Environment habitat specificity Dispersal