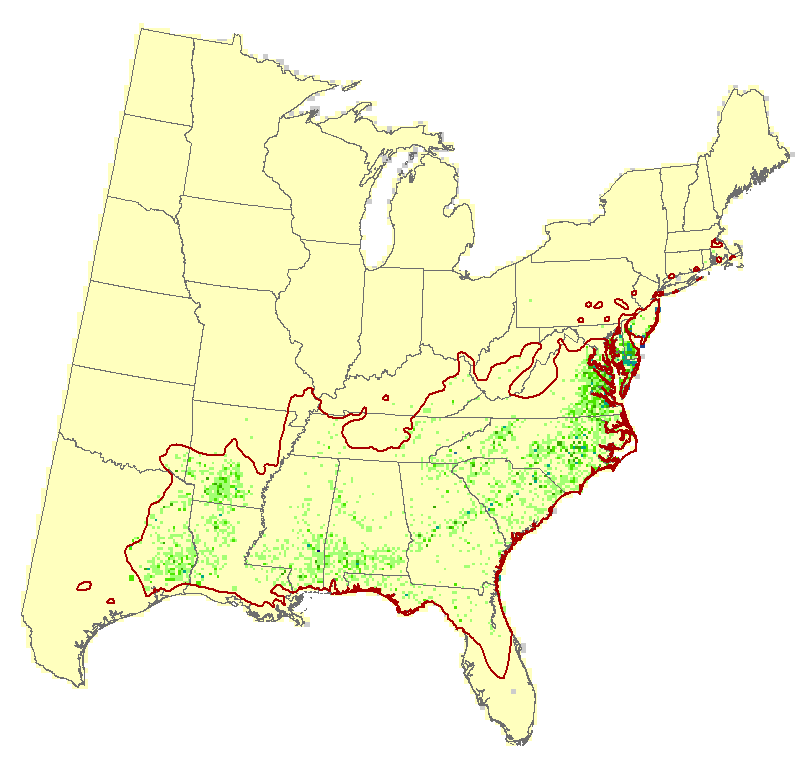
American holly (Ilex opaca)
Model Reliability: Medium
| GCM SCENARIO | % Area Occ | Ave IV | Sum IV | Future/Current IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | 8.1 | 2.4 | 5695 | N/A |
| RFimp | 8 | 1.7 | 4118 | 0.72 |
| CCSM45 | 16.8 | 1.4 | 7143 | 1.73 |
| CCSM85 | 22.1 | 1.4 | 8887 | 2.16 |
| GFDL45 | 22 | 1.4 | 8751 | 2.12 |
| GFDL85 | 25 | 1.3 | 9658 | 2.35 |
| HAD45 | 18.4 | 1.4 | 7715 | 1.87 |
| HAD85 | 21.3 | 1.4 | 8508 | 2.07 |
| GCM45 | 22.5 | 1.2 | 7869 | 1.91 |
| GCM85 | 25.7 | 1.2 | 9018 | 2.19 |
Regional Summary Tree Tables
Summaries for tree species are available for a variety of geographies, in both PDF and Excel format. These summaries are based on Version 4 of the Climate Change Tree Atlas
Interpretation Guide
American holly is sparsely distributed (6.0% of area), with low IV, across the southern states, and its medium reliable model suggests and increasing amount of habitat throughout that region (though still classed as 'No change' because it is found in <10%, or rare, within the eastern US). Its adaptability rating is moderate. It ranks as fair for its capability to deal with a changing climate.
Family: Aquifoliaceae
Guild: persistent, slow-growing understory tolerant
Functional Lifeform: small evergreen tree
| 4.5 | -0.10 |
| 0.47 |  |
MODFACs
What traits will impact American holly's ability to adapt to climate change, and in what way?:
Primary Positive Traits
Shade tolerance Environment habitat specificity
Primary Negative Traits
Fire topkill