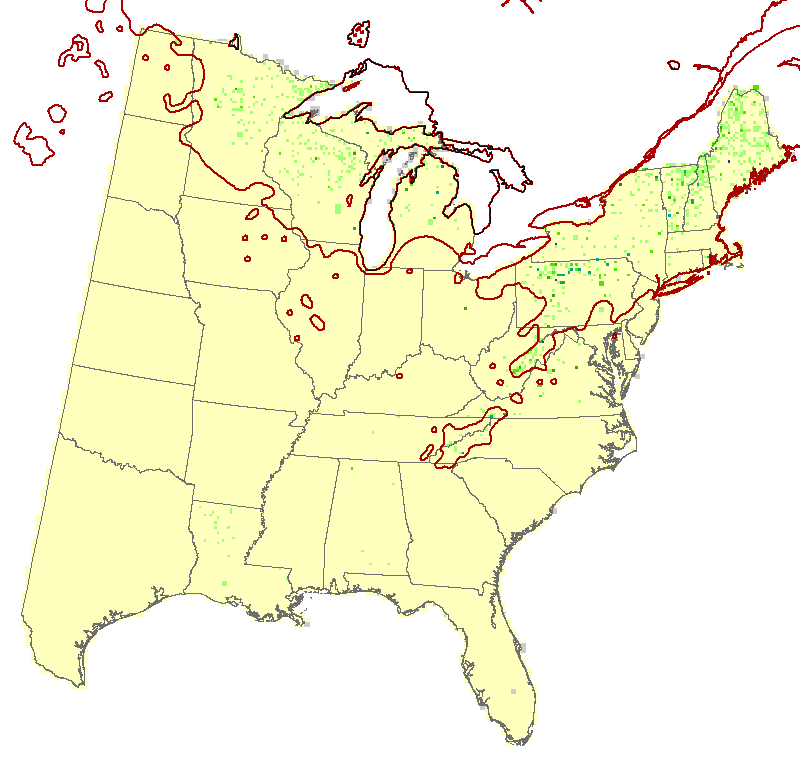
pin cherry (Prunus pensylvanica)
Model Reliability: Low
| GCM SCENARIO | % Area Occ | Ave IV | Sum IV | Future/Current IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | 3 | 2 | 1779 | N/A |
| RFimp | 2.6 | 1.1 | 836 | 0.47 |
| CCSM45 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 299 | 0.36 |
| CCSM85 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 178 | 0.21 |
| GFDL45 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 182 | 0.22 |
| GFDL85 | 3 | 0.1 | 96 | 0.11 |
| HAD45 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 231 | 0.28 |
| HAD85 | 4.9 | 0.1 | 111 | 0.13 |
| GCM45 | 7.7 | 0.1 | 238 | 0.28 |
| GCM85 | 7.4 | 0.1 | 128 | 0.15 |
Regional Summary Tree Tables
Summaries for tree species are available for a variety of geographies, in both PDF and Excel format. These summaries are based on Version 4 of the Climate Change Tree Atlas
Interpretation Guide
Pin cherry is narrowly distributed (2.2% of area), sparse, low IV, and rare across the north. It has a very poorly reliable model which appears meaningless; in fact, the model predicts potential suitable habitat in the south, nowhere near its current habitat. The species has been classed as moderately adaptable, and the overall capability rating is very poor. SHIFT shows neglibible influence.
Family: Rosaceae
Guild: pioneer, fast growing, short-lived, shade intolerant
Functional Lifeform: small deciduous tree
| 4.2 | 0.45 |
| -0.68 |  |
MODFACs
What traits will impact pin cherry's ability to adapt to climate change, and in what way?:
Primary Positive Traits
Seedling establishment Fire Regeneration Fire topkill
Primary Negative Traits
Shade tolerance