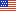
Leaf Beetles
Chrysomela spp. Linnaeus, 1758
Phratora spp. Chevrolat in Dejean, 1836
Altica spp. Geoffroy, 1762
Host(s) in the Alaska: birch (Betula spp.), willow (Salix spp.), quaking aspen (Popolus tremuloides), balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera), many other hardwoods & shrubs.
General Distribution in Alaska: Throughout the range of hosts statewide.
Current Status & Distribution in Alaska (2024)
Overall leaf beetle activity was low across the state in 2024.
Ground Detection Survey Observations: 13 observations were recorded during GDS. The number of trees damaged per plot varied from a single tree impacted to 30 trees impacted and severity was most commonly trace to 35% within tree damage. Leaf beetle damage was found on most hardwood hosts throughout the state.
ADS Observations: None.
iNaturalist Observations: None.
Historic Activity
No notable leaf beetle damage was observed in 2022.
In 2021, there were normal levels of leaf beetle damage in Interior Alaska. Unusual amounts of damage caused by leaf beetles were observed on birch in Southcentral in 2021 suggesting there could be an impact to leafminers due to competition for host resources.
Scattered pockets of cottonwood defoliation were observed in several parts of the state in 2019 (approximately 1,500 acres statewide), though most could not be ground checked to confirm the cause. Cottonwood leaf beetle (Chrysomela spp.) was noted as the damage agent on about 500 acres along Turnagain Arm in Southcentral Alaska this year. Cottonwood leaf beetle may be the causal agent in the remaining cases, although there are several species of defoliators that feed on cottonwood throughout the state.
The most commonly encountered leaf beetle in Alaska is locally known as the “cottonwood leaf beetle,” a name which actually represents members of several species of leaf beetle in the Macrolina subgenus of Chrysomela. The members of this subgenus are notoriously difficult to identify, but in Alaska Macrolina is thought to largely include C. falsa and C. mainensis. Black cottonwood (Populus balsamifera trichocarpa) is the predominant host of C. falsa in Alaska, though beetles also have been observed feeding on balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera balsamifera), quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides), and willows (Salix spp.). Less is known about C. mainensis, though it may predominantly breed on alders (Alnus spp.) and occasionally willows, cottonwood, and balsam poplar (Wilcox 1972, Clark et al. 2004).
Adult cottonwood leaf beetles are typically small, black insects that have orange markings on their elytra (forewings). These orange patterns vary considerably and may be hard to see on some beetles. The beetles average about 1/4-inch long. Males are usually slightly smaller than females. Adult beetles appear first in May when they emerge from their overwintering sites. They fly to cottonwoods and other hosts just after the leaves have come out. Throughout May to early June, the beetles are found on leaves and along twigs and branches. Shortly after mating, the females lay clusters of 15 to 75 pale, yellow eggs on the undersides of the leaves. Eggs begin to hatch by mid-June and small black larvae emerge and begin feeding on the undersides of the leaves. As they grow older, the larvae migrate as a group to the upper leaf surface and continue to feed throughout the month of July. When the larvae are disturbed, they inflate small, white glands that give off a pungent odor. By the end of July, the larvae firmly attach their skin to the upper leaf surface and form small black cocoons. Their pupal stage lasts for about one week and new adults emerge by mid-August. Adults leave the host plants by late August, seek cover, and hibernate for the winter.
Leaf beetle damage is usually not serious. Trees are rarely killed or weakened by this insect. Adults feed along the outer margins of leaves in the spring. Larvae consume everything but the larger veins of the leaf during the summer. Heavily infested trees will appear scorched by the end of the summer after the larvae have finished feeding. Although skeletonized leaves can be found throughout the crowns of affected trees, leaf beetle damage is usually much heavier in the tops of trees. The same trees are likely to be attacked repeatedly. Beetle populations will fluctuate considerably from year to year.
Although the cottonwood leaf beetle does not seriously affect trees growing in the forest, trees in urban areas may be more susceptible to the pest. Urban owners of ornamental cottonwoods should insure the best possible growing conditions so that the trees can withstand periodic heavy defoliation. Care should be taken to avoid injuring the roots with mechanical devices or soil compaction. To avoid moisture stress, trees should receive adequate water throughout the growing season. The factors that regulate leaf beetle populations are not well known, but heavy mortality in overwintering sites appears to be one of them. Beetles probably overwinter near the trees they fed on during the previous summer-either beneath loose bark flakes or on the ground near the tree. If damage has been heavy during the summer, the homeowner can help reduce the overwintering population by disturbing the litter layer with a rake or overturning material on the ground which may harbor the hibernating beetles. Summers characterized by heavy rainfall appear to have few leaf beetle problems. Heavy rainfall may dislodge many of the larvae. Consequently, a high-pressure water spray would be effective against small larvae as they begin to feed in the spring. Currently, no insecticides are registered specifically for use against the leaf beetle.
Clark, S. M., D. G. LeDoux, T. N. Seeno, E. G. Riley, A. J. Gilbert, and J. M. Sullivan. 2004. Host plants of leaf beetle species occurring in the United States and Canada (Coleoptera: Prsodacnidae, Megalopodidae, Chrysomelidae exclusive of Bruchinae). Special publication of the Coleopterists Society No. 2.
Wilcox, John A. 1972. A review of the North American Chrysomeline leaf beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). The University of the State of New York, State Museum and Science Service, Bulletin 421.
For more information on this agent, please contact Jessie Moan, Entomologist, U.S. Forest Service, at mary.moan@usda.gov.