About the Area
The 1.856-million-acre Coconino National Forest, one of six national forests in Arizona, features elevations ranging from 2,600 feet to the highest point in Arizona at 12,633 feet (Humphrey's Peak).
The area was originally established in 1898 as the "San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve." It was officially designated a National Forest by Pres. Theodore Roosevelt on July 2, 1908, when the reserve was merged with lands from other surrounding forest reserves to create today's Coconino National Forest.
The Coconino National Forest contains diverse landscapes, including deserts, ponderosa pine forests, flatlands, mesas, alpine tundra and ancient volcanic peaks. The forest surrounds the towns of Sedona and Flagstaff and borders four other national forests; the Kaibab National Forest to the west and northwest, the Prescott National Forest to the southwest, the Tonto National Forest to the south, and the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forests to the southeast.
The forest contains all or parts of 10 designated wilderness areas, including the Kachina Peaks Wilderness, which includes the summit of the San Francisco Peaks.
The Coconino National Forest consists of three districts: the Flagstaff Ranger District, Mogollon Rim Ranger District, and Red Rock Ranger District. Ranger stations for the aforementioned districts are located in Flagstaff, Happy Jack and Sedona. The headquarters, or Supervisor’s Office, is in Flagstaff.
Statistics
- Size: 1,843,608 acres
- Districts: 3
- Designated Wilderness Areas: 10 (The forest contains all or parts of these areas.)
- Full-time Employees: 230 to 280
- Developed Campgrounds: 24
- Cabin Rentals: 4
- Archaeological/Heritage Sites: 4
- Annual Visitors: 5.532 million (based on 2020 National Visitor Use Monitoring report)
- Fire Lookouts: 10
- Miles of Open Forest Roads: Approx. 3,300
- Miles of Trails on Forest: 693
- Number of Trails on Forest: 161
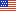
The 849,249 acres of the Flagstaff Ranger District surround the Flagstaff area, from Mormon Lake and Anderson Mesa to just north of the San Francisco Peaks, which dominate the area's volcanic highlands. At 12,633 feet, Humphreys Peak is the highest elevation in Arizona. Three of the summits that ring this dormant volcano's now quiet inner caldera are higher than any other mountain in the state. Geological evidence of the San Francisco Peaks suggest this was once one mountain with a peak of 15,000-16,000 feet before explosive eruptions and erosion sculpted the mountain range into the multiple peaks we see today.
The Flagstaff Ranger District is marked by expansive ponderosa pine forests and pinyon/juniper woodlands clustered around broad prairies and small lakes. Arizona's largest natural lake, Mormon Lake, is located here. The area is also known for its plentiful wildlife, including elk herds, bald eagles, ospreys and pronghorn antelope.
The San Francisco Peaks
The San Francisco Peaks are sacred to the native peoples that live in the area and its soaring profile set against a blue Arizona sky serves as a source of awe to contemporary residents and visitors. Views from the summit of the San Francisco Peaks stretch to the Grand Canyon's North Rim more than 80 miles away.
In the 1500s, the Spanish Conquistadors explored the area searching for gold and came upon the peaks and named them “Sierra Sinagua,” meaning "Mountains Without Water." The name didn’t stick, because they left the area quickly in search of the Grand Canyon and other gold. In 1629, Franciscan Friars who were conducting missionary work with Natives of the area named the mountain “San Francisco Peak” in honor of Patron Saint Francis of Assisi. In 1853 a man by the name of Amiel Whipple, who was leading expeditions in the area to find possible routes for a railroad across the continent dubbed the mountain range “San Francisco Cone,” but that name was never official and early maps still had the mountain printed as “San Francisco Peak.” On many maps today, the official name is printed as “San Francisco Mountain,” but many people either call it “The Peaks” or “San Francisco Peaks.”
The Navajo Tribe refers to the San Francisco Peaks as "Dook'o'oosłííd," which means "the summit which never melts" or "the mountain which peak never thaws." The following names refer to the San Francisco Peaks according to each respective Tribe:
- Tsii Bina — Aa'ku —(Acoma)
- Dził Tso — Dilzhe’e— (Apache)
- Hvehasahpatch or Huassapatch — Havasu 'Baaja — (Havasupai)
- Nuva'tukya'ovi — (Hopi)
- Wik'hanbaja—Hwal`bay — (Hualapai)
- 'Amat 'Iikwe Nyava — Hamakhav — (Mojave)
- Dook'o'oosłííd; Diné (Navajo)
- Nuvaxatuh — Nuwuvi — (Southern Paiute)
- Sierra sin Agua — (Spanish)
- Wi:mun Kwa — (Yavapai)
- Sunha K'hbchu Yalanne — A:shiwi (Zuni)
At 506,840 acres, the Mogollon Rim Ranger District is a rugged escarpment that forms the southern limit of the Colorado Plateau. It extends across the entire forest and provides excellent views within Plateau Country and Desert Canyon Country as well. Dropping as much as 2,000 feet in some areas, the Rim provides some of the most far-reaching scenery in Arizona. Views stretch from its rocky precipice to Four Peaks of the Mazatzals northeast of Phoenix.
Needless to say, sightseeing is a favorite activity along the Rim, but this forest area also boasts a historic system of hiking and horseback trails, a couple of picturesque lakes for boating and fishing, and backcountry skiing for wilderness adventurers. The Rim Road (Forest Road 300) is among one of the most popular forest roads in northern Arizona due to running along the edge of the Mogollon Rim for miles, offering spectacular sights above the valley below.
The Red Rock Ranger District includes 487,519 acres of magnificent splendor. Sedona's colorful collection of buttes, pinnacles, mesas and canyons is famous for its red rock vistas. Over the years, this area has served as the setting of many western novels and movies and has been the subject of uncounted paintings, photographs, and other works of art. The remains of ancient wetlands, these crimson cliffs have been carved by the forces of the desert into one of nature's most magnificent masterpieces.
No matter what you do in Red Rock Country, you're always sightseeing. Ways to get even closer to all this scenery includes: hiking, horseback riding, taking a scenic drive, sliding down a natural waterslide, picnicking, camping, taking lots of photos and fishing in Oak Creek. Everywhere you look in this district seems to resemble a beautiful post card or painting.